洛谷P1525-关押罪犯-题解
【NOIP2010 提高组】 关押罪犯
题目描述
S 城现有两座监狱,一共关押着 名罪犯,编号分别为 。他们之间的关系自然也极不和谐。很多罪犯之间甚至积怨已久,如果客观条件具备则随时可能爆发冲突。我们用“怨气值”(一个正整数值)来表示某两名罪犯之间的仇恨程度,怨气值越大,则这两名罪犯之间的积怨越多。如果两名怨气值为 的罪犯被关押在同一监狱,他们俩之间会发生摩擦,并造成影响力为 的冲突事件。
每年年末,警察局会将本年内监狱中的所有冲突事件按影响力从大到小排成一个列表,然后上报到 S 城 Z 市长那里。公务繁忙的 Z 市长只会去看列表中的第一个事件的影响力,如果影响很坏,他就会考虑撤换警察局长。
在详细考察了 名罪犯间的矛盾关系后,警察局长觉得压力巨大。他准备将罪犯们在两座监狱内重新分配,以求产生的冲突事件影响力都较小,从而保住自己的乌纱帽。假设只要处于同一监狱内的某两个罪犯间有仇恨,那么他们一定会在每年的某个时候发生摩擦。
那么,应如何分配罪犯,才能使 Z 市长看到的那个冲突事件的影响力最小?这个最小值是多少?
输入格式
每行中两个数之间用一个空格隔开。第一行为两个正整数 ,分别表示罪犯的数目以及存在仇恨的罪犯对数。接下来的 行每行为三个正整数 ,表示 号和 号罪犯之间存在仇恨,其怨气值为 。数据保证 ,且每对罪犯组合只出现一次。
输出格式
共 行,为 Z 市长看到的那个冲突事件的影响力。如果本年内监狱中未发生任何冲突事件,请输出 0。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
4 6
1 4 2534
2 3 3512
1 2 28351
1 3 6618
2 4 1805
3 4 12884样例输出 #1
3512提示
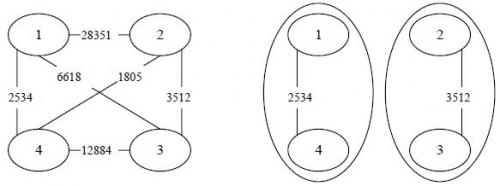
【输入输出样例说明】罪犯之间的怨气值如下面左图所示,右图所示为罪犯的分配方法,市长看到的冲突事件影响力是 (由 号和 号罪犯引发)。其他任何分法都不会比这个分法更优。
【数据范围】
对于 的数据有 。
对于 的数据有 。
对于 的数据有 。
P1525 [NOIP2010 提高组] 关押罪犯 - 洛谷
思路一
考虑到这题要我们求出最小的影响力,很自然的就想到贪心。那么怎么贪应该不需要我来教,是人都会贪 (当然,做人太贪心可不是好事)。 贪心的思路就是:将图按照权值从大到小排序,考虑每一条边,如果能使这条边的两点分别在两个集合(树)里,那么就将两个点所在的集合(树)合并成一个集合(森林合成树),否则输出这条边的权值。 即,当两点已经在一个集合中的时候,这两点会引起冲突,此时引起的冲突也是最大的冲突了。
C++ 代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <numeric>
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
class UnionFindSet {
vector<T> trees, size;
public:
explicit UnionFindSet(const T &len = 0) : trees(len * 2), size(len * 2, 1) {
iota(trees.begin(), trees.begin() + len, len);
iota(trees.begin() + len, trees.end(), len);
}
int find(const T &x) {
T tmp;
for (tmp = x; trees[tmp] != tmp; tmp = trees[tmp]);
return tmp;
}
void unite(const T &x, const T &y) {
T &&fx = find(x), &&fy = find(y);
size[fx] <= size[fy] ? trees[fx] = fy : trees[fy] = fx;
if (size[fx] == size[fy] and fx != fy)
size[fy]++;
}
void earse(const T &x) {
--size[find(x)];
trees[x] = x;
}
void move(const T &x, const T &y) {
T &&fx = find(x), &&fy = find(y);
if (fx == fy) return;
trees[x] = fy;
--size[fx], ++size[fy];
}
};
struct pos {
int x, y, z;
};
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr), cout.tie(nullptr);
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
UnionFindSet<int> ufs(n + 1);
vector<pos> people(m);
vector<int> enemy(m + 1, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
cin >> people[i].x >> people[i].y >> people[i].z;
sort(people.begin(), people.end(),
[](const pos &a, const pos &b) { return a.z > b.z; });
auto buildShip = [&](int &form, int &to) {
if(not form)
form = to;
else
ufs.unite(form, to);
};
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
int &&x = ufs.find(people[i].x), &&y = ufs.find(people[i].y);
if (x == y) {
cout << people[i].z;
return 0;
}
buildShip(enemy[people[i].x], people[i].y);
buildShip(enemy[people[i].y], people[i].x);
}
cout.put('0');
return 0;
}思路二(8月5日更新)
思路二用到了种类并查集,将两个开一个两倍长的并查集表示两个监狱,剩下大体思路和上面一样。
C++代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <numeric>
template<typename T>
class UnionFindSet {
std::vector<T> trees, size;
public:
explicit UnionFindSet(T len) : trees(len << 1), size((len << 1), 1) {
std::iota(trees.begin(), trees.begin() + len, len);
std::iota(trees.begin() + len, trees.end(), len);
}
T find(const T &x) {
return trees[x] == x ? x : trees[x] = find(trees[x]);
}
void unite(const T &x, const T &y) {
T &&fx = find(x), &&fy = find(y);
if (fx == fy) return;
if (size[fx] < size[fy]) std::swap(fx, fy);
trees[fy] = fx;
size[fx] += size[fy];
}
void erase(const T &x) {
--size[find(x)];
trees[x] = x;
}
void move(const T &x, const T &y) {
T &&fx = find(x), &&fy = find(y);
if (fx == fy) return;
trees[x] = fy;
--size[fx], ++size[fy];
}
bool isSameSet(const T &x, const T &y) {
return find(x) == find(y);
}
};
struct pos {
int x, y, z;
};
using namespace std;
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr), std::cout.tie();
int n, m, ans = 0;
cin >> n >> m;
UnionFindSet<int> ufs((n + 1) << 1);
vector<pos> people(m);
vector<int> enemy(m + 1, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
cin >> people[i].x >> people[i].y >> people[i].z;
sort(people.begin(), people.end(),
[](const pos &a, const pos &b) { return a.z > b.z; });
auto getEnemy = [&](const int &x) {
return x + n;
};
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
int &x = people[i].x, &y = people[i].y;
if (ufs.isSameSet(x, y) or ufs.isSameSet(getEnemy(x), getEnemy(y))) {
cout << people[i].z;
return 0;
}
ufs.unite(getEnemy(x), y);
ufs.unite(x, getEnemy(y));
}
cout.put('0');
return 0;
}