洛谷P3958-奶酪-题解
【NOIP2017 提高组】 奶酪
题目背景
NOIP2017 提高组 D2T1
题目描述
现有一块大奶酪,它的高度为 ,它的长度和宽度我们可以认为是无限大的,奶酪中间有许多半径相同的球形空洞。我们可以在这块奶酪中建立空间坐标系,在坐标系中,奶酪的下表面为 ,奶酪的上表面为 。
现在,奶酪的下表面有一只小老鼠 Jerry,它知道奶酪中所有空洞的球心所在的坐标。如果两个空洞相切或是相交,则 Jerry 可以从其中一个空洞跑到另一个空洞,特别地,如果一个空洞与下表面相切或是相交,Jerry 则可以从奶酪下表面跑进空洞;如果一个空洞与上表面相切或是相交,Jerry 则可以从空洞跑到奶酪上表面。
位于奶酪下表面的 Jerry 想知道,在不破坏奶酪的情况下,能否利用已有的空洞跑 到奶酪的上表面去?
空间内两点 、 的距离公式如下:
输入格式
每个输入文件包含多组数据。
第一行,包含一个正整数 ,代表该输入文件中所含的数据组数。
接下来是 组数据,每组数据的格式如下: 第一行包含三个正整数 ,两个数之间以一个空格分开,分别代表奶酪中空洞的数量,奶酪的高度和空洞的半径。
接下来的 行,每行包含三个整数 ,两个数之间以一个空格分开,表示空洞球心坐标为 。
输出格式
行,分别对应 组数据的答案,如果在第 组数据中,Jerry 能从下表面跑到上表面,则输出 Yes,如果不能,则输出 No。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
3
2 4 1
0 0 1
0 0 3
2 5 1
0 0 1
0 0 4
2 5 2
0 0 2
2 0 4样例输出 #1
Yes
No
Yes提示
【输入输出样例 说明】
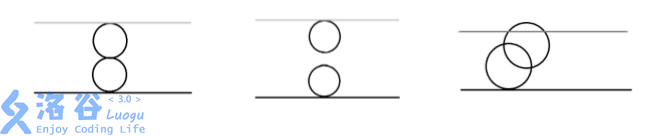
第一组数据,由奶酪的剖面图可见:
第一个空洞在 与下表面相切;
第二个空洞在 与上表面相切;
两个空洞在 相切。
输出 Yes。
第二组数据,由奶酪的剖面图可见:
两个空洞既不相交也不相切。
输出 No。
第三组数据,由奶酪的剖面图可见:
两个空洞相交,且与上下表面相切或相交。
输出 Yes。
【数据规模与约定】
对于 的数据,,,,坐标的绝对值不超过 。
对于 的数据,,,,坐标的绝对值不超过 。
对于 的数据,,,坐标的绝对值不超过 。
对于 的数据,,,,坐标的绝对值不超过 。
思路
搜索
看到从一个点到另一个点,很容易就想到使用搜索算法了。这题数据量比较小,搜索时间复杂度也不会被卡,正向搜索和反向搜索都可以过。简单来说就是,枚举每个下表面上的点(或者上表面上的点),每次从这个点出发,搜索,如果能搜索到上表面的点(或者下表面上的点),则说明可以走通,有解。
C++代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <numeric>
using namespace std;
using i64 = long long;
struct pos {
i64 x, y, z;
};
vector<bool> visited;
vector<pos> poss;
i64 t, n, h, r;
bool isNear(const pos &first, const pos &second) {
return (first.x - second.x) * (first.x - second.x)
+ (first.y - second.y) * (first.y - second.y)
+ (first.z - second.z) * (first.z - second.z)
<= 4 * r * r;
}
bool isYes = false;
void dfs(const i64 &begin) {
if (isYes or visited[begin])
return;
visited[begin] = true;
if (poss[begin].z + r >= h) {
isYes = true;
return;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
if (not visited[i] and isNear(poss[begin], poss[i]))
dfs(i);
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr), cout.tie(nullptr);
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
cin >> n >> h >> r;
isYes = false;
vector<i64> starts;
poss.resize(n + 1);
visited.resize(n + 1);
fill(visited.begin(), visited.end(), false);
for (i64 i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
cin >> poss[i].x >> poss[i].y >> poss[i].z;
if (poss[i].z <= r)
starts.emplace_back(i);
}
for (auto &i: starts)
dfs(i);
cout << (isYes ? "Yes\n" : "No\n");
}
return 0;
}并查集
除了搜索以外,我们也可以用并查集来进行查找,预先将和设为底面和顶面,然后先将底面和顶面的节点合并到和所在的集合里,紧接着遍历每个点和其他点,如果相邻就合并。最后判断和是否在一个集合里即可
C++代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <numeric>
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
class UnionFindSet {
vector<T> trees, size;
public:
explicit UnionFindSet(const T &len = 0) : trees(len * 2), size(len * 2, 1) {
iota(trees.begin(), trees.begin() + len, len);
iota(trees.begin() + len, trees.end(), len);
}
int find(const T &x) {
T tmp;
for (tmp = x; trees[tmp] != tmp; tmp = trees[tmp]);
return tmp;
}
void unite(const T &x, const T &y) {
T &&fx = find(x), &&fy = find(y);
size[fx] <= size[fy] ? trees[fx] = fy : trees[fy] = fx;
if (size[fx] == size[fy] and fx != fy)
size[fy]++;
}
void earse(const T &x) {
--size[find(x)];
trees[x] = x;
}
void move(const T &x, const T &y) {
T &&fx = find(x), &&fy = find(y);
if (fx == fy) return;
trees[x] = fy;
--size[fx], ++size[fy];
}
};
using i64 = long long;
struct pos {
i64 x, y, z;
};
bool isNear(const pos &first, const pos &second, const i64 &r) {
return (first.x - second.x) * (first.x - second.x)
+ (first.y - second.y) * (first.y - second.y)
+ (first.z - second.z) * (first.z - second.z)
<= 4 * r * r;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr), cout.tie(nullptr);
i64 t, n, h, r;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
cin >> n >> h >> r;
UnionFindSet<i64> ufs(n + 3);
vector<i64> xs(n + 1), ys(n + 1), zs(n + 1);
for (i64 i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
cin >> xs[i] >> ys[i] >> zs[i];
if (zs[i] <= r)
ufs.unite(i, n + 1);
if (zs[i] + r >= h)
ufs.unite(i, n + 2);
}
for (i64 i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
for (i64 j = i + 1; j <= n; ++j)
if (isNear({xs[i], ys[i], zs[i]}, {xs[j], ys[j], zs[j]}, r))
ufs.unite(i, j);
cout << (ufs.find(n + 1) ^ ufs.find(n + 2) ? "No\n" : "Yes\n");
}
return 0;
}