NCST-暑期基础培训-第四周排位赛-题解
A 简单的倍增
题目描述
我们知道倍增的核心是 , 我们知道 的涵义是从 出发,走 步到达的下标。即 , 第一维即为起点,第二维为步数,第二维使用 的次方表示步数,即为倍增,现在定义二进制拆分为将一个数字拆分为 的次方的组合,例如 可以拆分为即为拆分的结果,题目将给定一些数字,请你从小到大输出对应每个数字对应二进制拆分的结果。
输入
第一行包含一个正整数 ,表示给定数字的数目。
之后的t行,每行给出一个具体的正整数 。
输出
输出包含 行,每行包含一组 的次方的组合。
样例输入
4
3
8
12
10000样例输出
1 2
8
4 8
16 256 512 1024 8192Contest Problems - Online Judge System
思路
这题应该是一道签到题,可以用递增的表达式来算,也可以直接用数学暴力算
C++代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
void work(int a) {
vector<int> ans(int(log2(a)) + 1);
int n = 0;
for (int bin; a; a -= (1 << bin)) {
bin = int(log2(a));
ans[n++] = 1 << bin;
}
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i)
cout << ans[i] << ' ';
cout.put('\n');
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr), cout.tie(nullptr);
int t, a;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
cin >> a;
work(a);
}
return 0;
}B 简单的括号匹配
题目描述
有一个表达式,它由字母,运算符 +、-、*、/ 和小括号构成,并且表达式以符号@为结尾。
现在请你编写程序,检验表达式中的括号是否匹配。
输入
输入一行,表示这个表达式
输出
如果表达式中的括号匹配,输出 YES,否则输出 NO
样例输入
(25+x)*(a*(a+b+b)@样例输出
NO提示
很明显样例中缺少 ‘)’
数据范围:表达式长度小于100
Contest Problems - Online Judge System
##思路
后缀表达式乞丐版
C++代码
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s;
getline(cin, s, '@');
stack<char> sta;
for (auto &i: s) {
if (i == '(')
sta.emplace('(');
else if (i == ')') {
if (not sta.empty())
sta.pop();
else {
cout << "NO";
return 0;
}
}
}
cout << (sta.empty() ? "YES" : "NO");
return 0;
}C 简单的马走日
题目描述
众所周知,象棋中马是以日字形进行移动的。
现在给你一个 大小的棋盘,以及初始马的位置,请问你在不能重复经过棋盘上的同一个点的情况下,计算马有多少途径遍历棋盘上所有的点。
输入
第一行输入一个整数 ,表示数据组数
接下来 行,为四个整数,表示棋盘大小 和初始马的位置
输出
每组测试数据包含一行,为一个整数,表示马能遍历棋盘的途径总数,若无法遍历棋盘上的所有点则输出
样例输入
1
5 4 0 0样例输出
32提示
样例解释:马在初始位置 的情况下,有 种方式遍历棋盘上所有的点,并且每次遍历每个点只被遍历一次
数据范围:
思路
带回溯的dfs
注意:
- 尽量一次性把空间就开完,别学我,每次都resize,提高空间利用率,结果TLE半天
C++代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
long long ans;
int n, m, target, dx[]{-2, -2, -1, -1, 1, 1, 2, 2},
dy[]{-1, 1, -2, 2, -2, 2, -1, 1};
bool visited[9][9];
void dfs(const int &x, const int &y, const int &step) {
if (step == target) {
++ans;
return;
}
visited[x][y] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
int &&px = x + dx[i], &&py = y + dy[i];
if (px >= 0 and py >= 0 and px < n and py < m and not visited[px][py]) {
dfs(px, py, step + 1);
visited[px][py] = false;
}
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr), cout.tie(nullptr);
int t, x, y;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
ans = 0;
cin >> n >> m >> x >> y;
target = n * m;
for(auto &i : visited)
for(auto &j : i)
j = false;
dfs(x, y, 1);
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}D 简单的树上距离
题目描述
如题,给定一棵有根多叉树,请求出指定两个点直接最近的公共祖先。
输入格式
第一行包含三个正整数 ,分别表示树的结点个数、询问的个数和树根结点的序号。
接下来 行每行包含两个正整数 ,表示 结点和 结点之间有一条直接连接的边(数据保证可以构成树)。
接下来 行每行包含两个正整数 ,表示询问 结点和 结点的最近公共祖先。
输出格式
输出包含 行,每行包含一个正整数,依次为每一个询问的结果。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
5 5 4
3 1
2 4
5 1
1 4
2 4
3 2
3 5
1 2
4 5样例输出 #1
4
4
1
4
4提示
对于 的数据,,。
对于 的数据,,。
对于 的数据,,,不保证 。
Contest Problems - Online Judge System
笔者附
这题是洛谷原题,洛谷题目描述还有以下内容
样例说明:
该树结构如下:
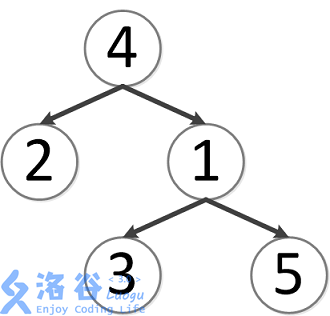
第一次询问: 的最近公共祖先,故为 。
第二次询问: 的最近公共祖先,故为 。
第三次询问: 的最近公共祖先,故为 。
第四次询问: 的最近公共祖先,故为 。
第五次询问: 的最近公共祖先,故为 。
故输出依次为 。
2021/10/4 数据更新 @fstqwq:应要求加了两组数据卡掉了暴力跳。
思路
这题是LCA的倍增实现或者tarjan算法,或者转换成RMQ问题用ST表都可以过
我不会写LCA的朴素算法以外的写法,这里就没写,后面学了会补上代码的
倍增算法实现
tarjan算法实现
C++代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <numeric>
using namespace std;
class UnionFindSet {
vector<size_t> trees;
public:
explicit UnionFindSet(const size_t &len) : trees(len) {
iota(trees.begin(), trees.end(), 0);
}
size_t find(const size_t &x) {
return trees[x] == x ? x : trees[x] = find(trees[x]);
}
//注意这里不能写启发式合并
void unite(const size_t &x, const size_t &y) {
size_t &&fx = find(x), &&fy = find(y);
if (fx == fy) return;
trees[fx] = fy;
}
};
//继承于并查集类,因为tarjan算法基于并查集的实现
class TreeLCA : UnionFindSet {
//记录节点是否访问过
vector<bool> isVisited;
//邻接表存树
vector<vector<int> > graph;
//存查询的信息 和 输入的顺序
vector<vector<pair<int, int> > > queries;
//存查询结果
vector<size_t> ans;
//tarjan算法
void tarjan(const size_t &index) {
//标记当前节点已走过
isVisited[index] = true;
//取出可以走的节点
for (auto &i: graph[index]) {
//如果走过了,那就不能再走了
if (isVisited[i])
continue;
//走这个节点
tarjan(i);
//当这条路走到尽头了,将走的节点和当前节点合并到集合中(注意合并顺序)
unite(i, index);
}
//查看有无当前节点相关的查询
for (auto &i: queries[index])
//如果有,并且查询的另一个节点也访问过了
if (isVisited[i.first])
//那么他们的公共祖先就是他们在并查集里的“代表人”
ans[i.second] = find(i.first);
}
public:
//继承并使用的构造函数
TreeLCA(size_t n, size_t m)
: isVisited(n), graph(n), queries(n), ans(m), UnionFindSet(n) {
//处理用户输入
size_t from, to;
while (--n) {
cin >> from >> to;
graph[--from].emplace_back(--to);
graph[to].emplace_back(from);
}
for (int &&i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
cin >> from >> to;
queries[--from].emplace_back(--to, i);
queries[to].emplace_back(from, i);
}
}
//返回查询的结果
vector<size_t> LCA(const size_t &root) {
tarjan(root);
return ans;
}
};
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(); cout.tie();
int n, m, s;
cin >> n >> m >> s;
TreeLCA tree(n, m);
for (auto &i : tree.LCA(--s))
cout << i + 1 << endl;
return 0;
}E 简单的堆的判断
将一系列给定数字顺序插入一个初始为空的小顶堆H[]。随后判断一系列相关命题是否为真。命题分下列几种:
x is the root:x是根结点;x and y are siblings:x和y是兄弟结点;x is the parent of y:x是y的父结点;x is a child of y:x是y的一个子结点。
输入格式:
每组测试第1行包含2个正整数N(≤ 1000)和M(≤ 20),分别是插入元素的个数、以及需要判断的命题数。下一行给出区间内的N个要被插入一个初始为空的小顶堆的整数。之后M行,每行给出一个命题。题目保证命题中的结点键值都是存在的。
输出格式:
对输入的每个命题,如果其为真,则在一行中输出T,否则输出F。
输入样例:
5 4
46 23 26 24 10
24 is the root
26 and 23 are siblings
46 is the parent of 23
23 is a child of 10输出样例:
F
T
F
TContest Problems - Online Judge System
笔者附
这题在 PTA | 程序设计类实验辅助教学平台 上也有原题
思路
直说了,手写堆,我不会(STL优先队列太好用了,以至于我不会它的原理,OOP的坏处了属于是)